Wheat value analysis and alternatives
Publish Time: 2025-07-07
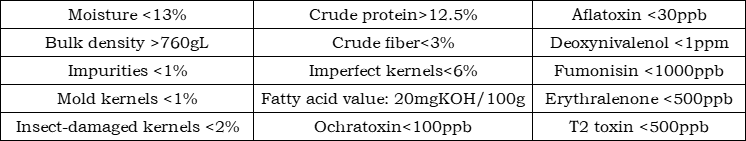
In 2020, especially since the second half of the year, the prices of raw materials such as corn, soybean meal, corn by-products, and wheat by-products have continued to rise, bringing huge cost pressure to feed companies and breeding companies. As of January 2021, the price of corn is close to 2,900 yuan/ton and the supply is tight, and the price of soybean meal is 3,550 yuan/ton, while the price of wheat, the main grain supply in the north, is 2,550 yuan/ton. As a feed raw material, its use value is outstanding, but wheat is different from corn in nutritional characteristics. When using it, you should pay attention to some matters. The following briefly summarizes the nutritional characteristics and usage plans of wheat for reference. 1. Wheat classification and nutritional characteristicsWheat is divided into winter wheat and spring wheat according to planting time; it is divided into red wheat, white wheat, and flower wheat according to skin color; it is divided into hard wheat and soft wheat according to wheat grain texture. The metabolic energy of wheat is 90% of that of corn, the protein is higher than corn, and the amino acid composition is more balanced than corn. In addition, wheat starch becomes viscous when it comes into contact with water. It is a natural binder and is conducive to granulation. At the same time, wheat starch has a lower gelatinization temperature and is easier to gelatinize. Wheat starch is 53-64℃, while corn starch is 61-72℃.Wheat contains about 6% non-starch polysaccharides (NSP), mainly arabinoxylan, glucan and xylose. It has strong viscosity and cannot be digested and absorbed by chickens. NSP can form a sticky gelatinous layer on the surface of the intestinal mucosa, affecting the digestibility of other nutrients in the feed. The absorption of macromolecules such as fat is most obviously hindered, which can easily lead to fat malabsorption syndrome. Due to poor digestion and absorption of nutrients, intestinal hypertonic water absorption causes broiler excrement to become thinner and more viscous, which endangers the health of broilers. NSP has a relatively small impact on pigs. Adding non-starch polysaccharide enzymes to wheat diets can solve the problem of non-starch polysaccharide absorption. The main factor affecting the palatability of wheat is infection with ergot toxins.2. Acceptance criteria for wheatSensory indicators: neat, full, uniform color, no fermentation, mildew, live insects, peculiar smell or odor. The skin of red wheat is dark red or reddish brown; the skin of white wheat is yellowish white or milky white.Required inspection indicators: moisture, bulk density, impurities, and mildew rate.Recommended acceptance criteria:Comparison table of conventional indicators of wheat, corn and soybean meal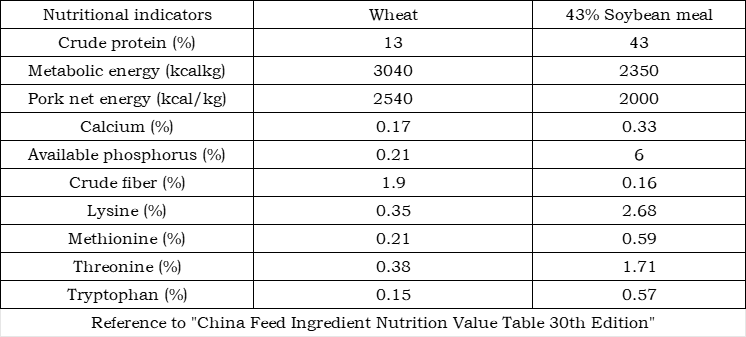 3. Recommended alternativesQ1—When the amount of wheat added is less than 10%, 100kg of wheat replaces 80-85kg of corn + 15-20kg of soybean meal, and no other adjustments are made;Q2—When the amount of wheat added is more than 10%, you can refer to the above-mentioned proportion to replace corn and soybean meal, but you need to rebalance the indicators such as amino acids, calcium, phosphorus, etc., and you need to supplement wheat complex enzymes mainly composed of xylanase and β-glucanase;Q3—When wheat is replaced in large proportions, laying hens and yellow-feathered broilers need to consider the supplementation of linoleic acid and lutein;Q4—When the amount of wheat used is too large, consider the change in the appearance color of the feed and the adjustment of the hardness of the pelletized particles;Q5—Some feed companies do not have wheat impurity removal equipment installed. When using it, be sure to consider the impurity content and do a good job of wheat impurity removal.
3. Recommended alternativesQ1—When the amount of wheat added is less than 10%, 100kg of wheat replaces 80-85kg of corn + 15-20kg of soybean meal, and no other adjustments are made;Q2—When the amount of wheat added is more than 10%, you can refer to the above-mentioned proportion to replace corn and soybean meal, but you need to rebalance the indicators such as amino acids, calcium, phosphorus, etc., and you need to supplement wheat complex enzymes mainly composed of xylanase and β-glucanase;Q3—When wheat is replaced in large proportions, laying hens and yellow-feathered broilers need to consider the supplementation of linoleic acid and lutein;Q4—When the amount of wheat used is too large, consider the change in the appearance color of the feed and the adjustment of the hardness of the pelletized particles;Q5—Some feed companies do not have wheat impurity removal equipment installed. When using it, be sure to consider the impurity content and do a good job of wheat impurity removal.